Fast urbanization and climate change require innovative systems for an efficient movement of people and goods in cities. As trends towards vehicle-sharing, autonomous vehicles, and the use of micro-mobility systems gain strength, the intersection of these fields appears as an area of great opportunity.
Autonomy could potentially bring the convenience of on-demand mobility into already prevalent shared micro-mobility systems (SMMS), increasing their efficiency and incentivizing more people to use active mobility modes. The novelty of introducing autonomous driving technology into SMMS and their inherent complexity requires tools to assess and quantify the potential impact of autonomy on fleet performance and user experience.
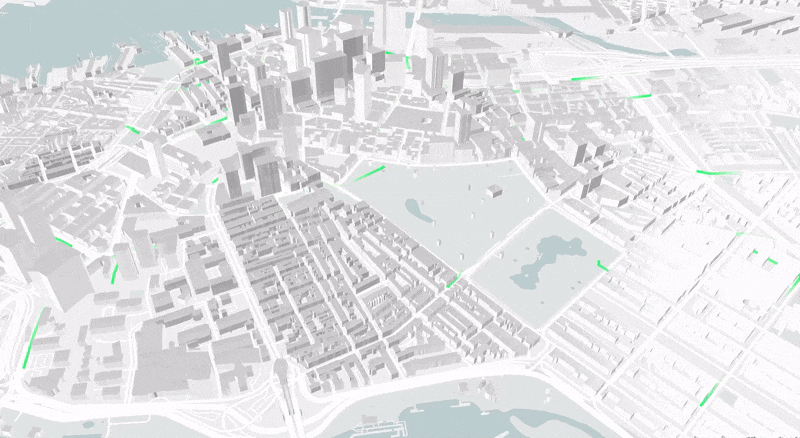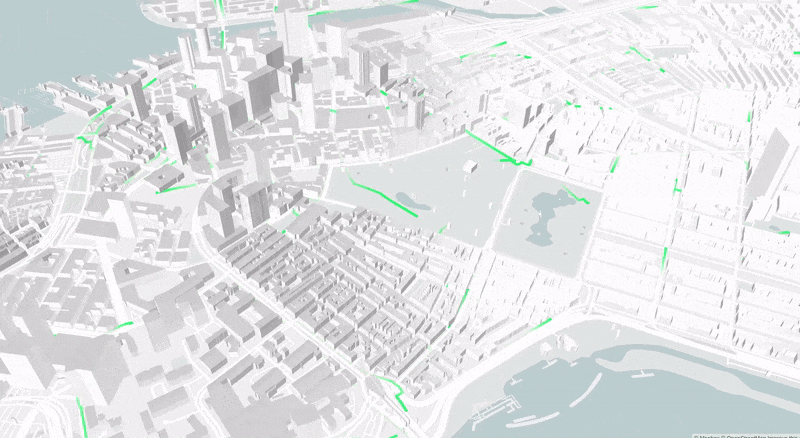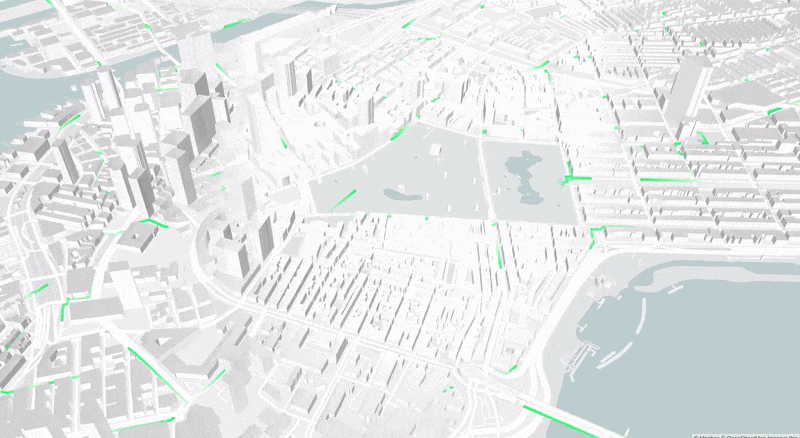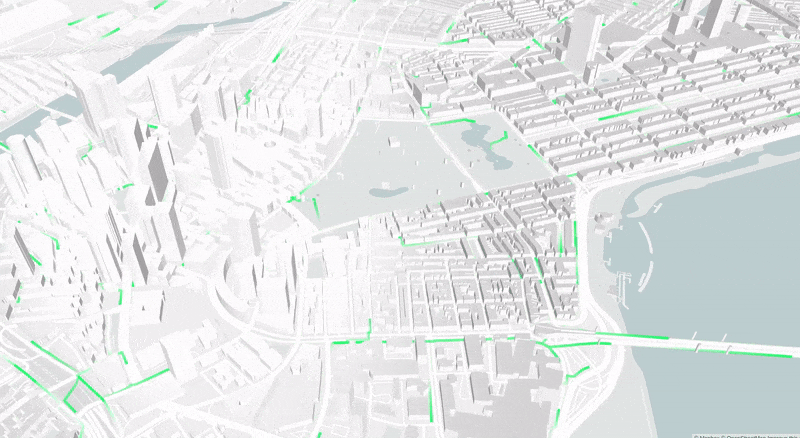
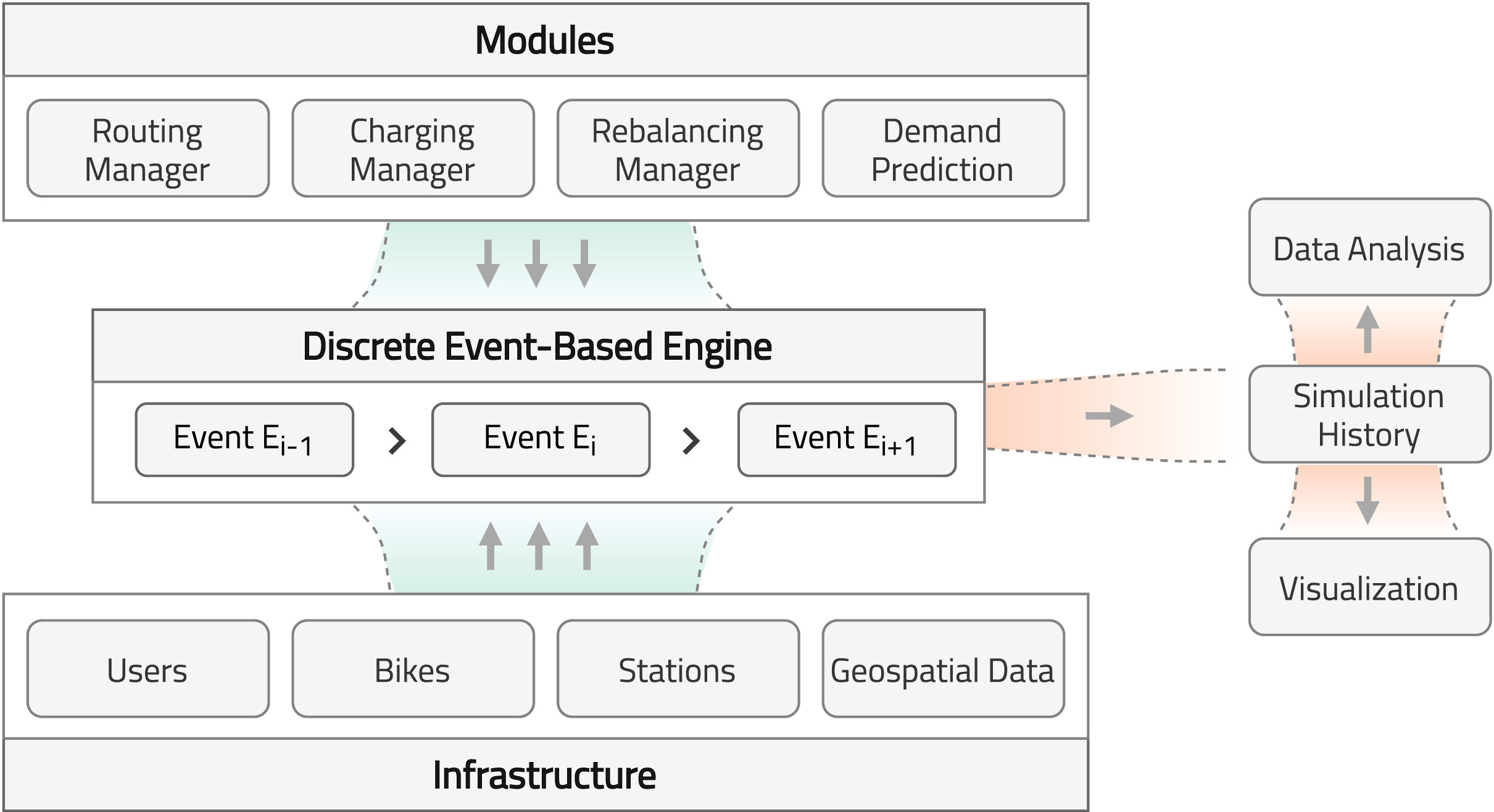
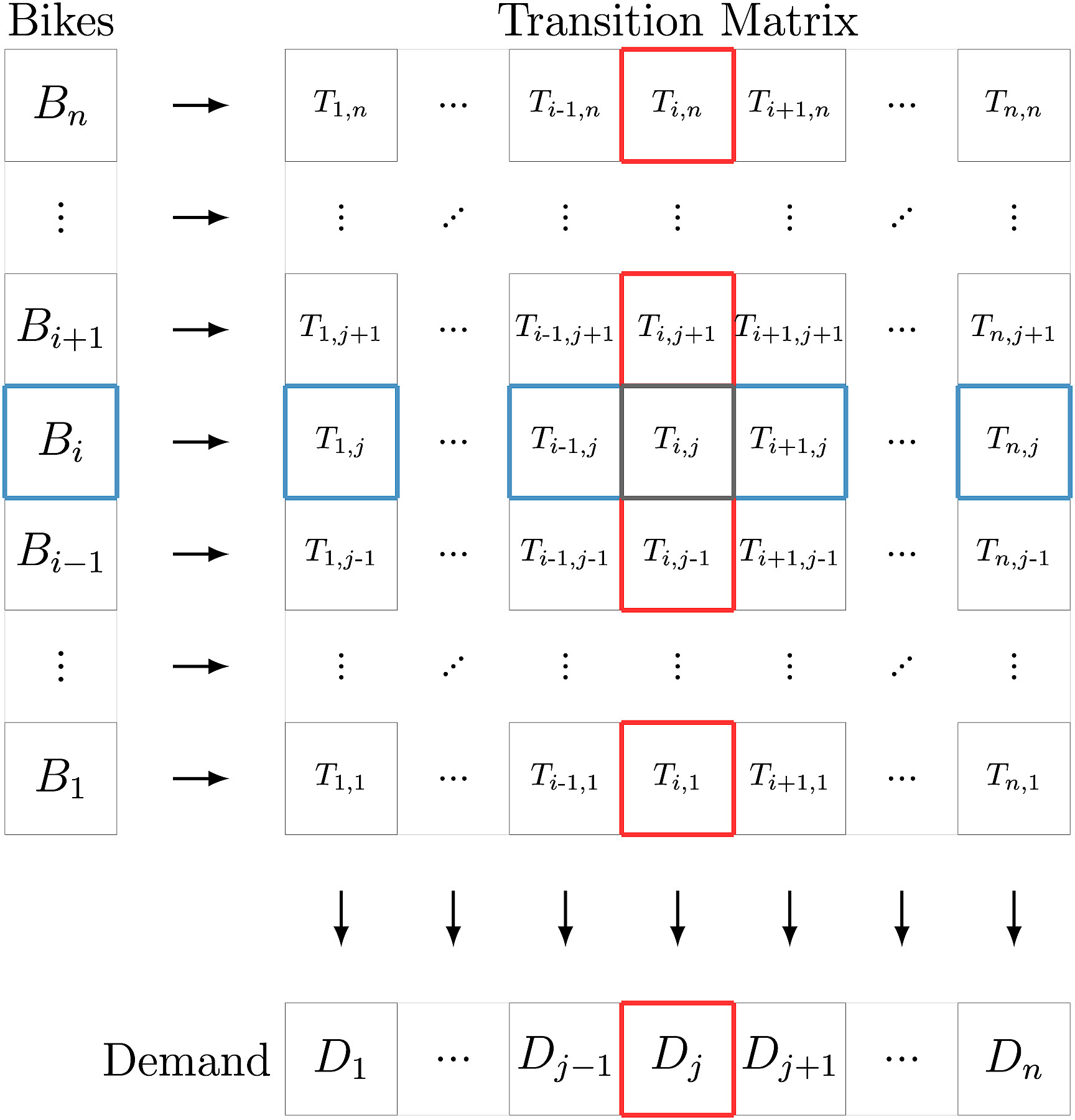
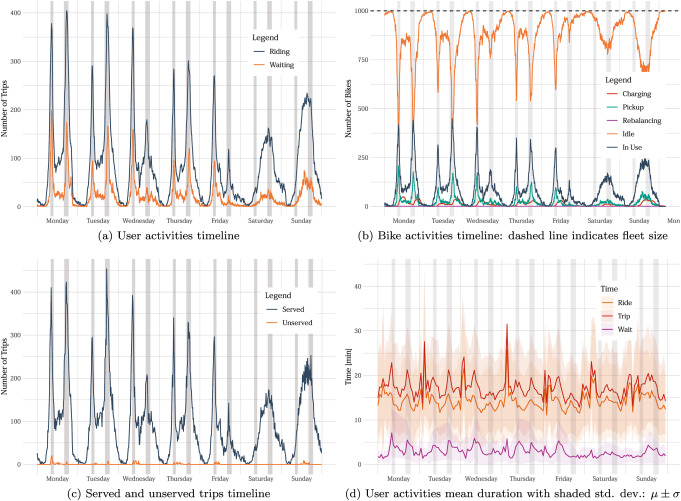
This paper presents an ad-hoc agent-based simulator for the assessment of the fleet behavior of autonomous SMMS in realistic scenarios, including a rebalancing system based on demand prediction. It also allows comparing its performance to station-based and dockless schemes.
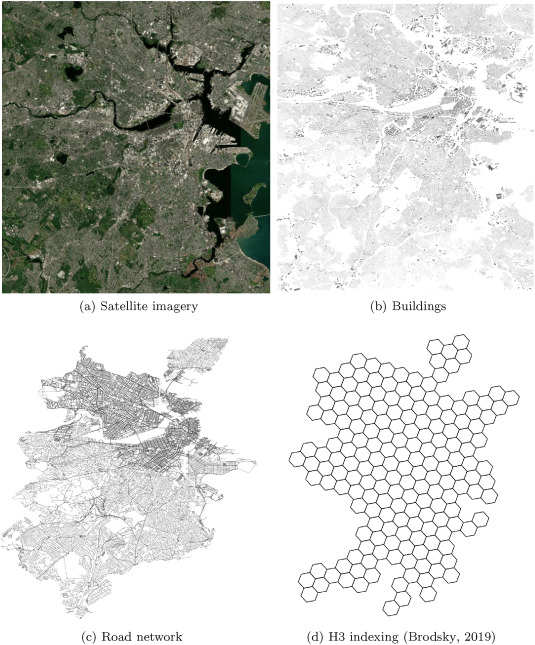
The proposed simulation framework is highly configurable and flexible and works with high resolution and precision geospatial data. The results of studies carried out with this simulation tool could provide valuable insights for many stakeholders, including vehicle design engineers, fleet operators, city planners, and governments.
Date |
May 2021
Technologies |
python
·
simpy
·
numpy
·
pandas
·
matplotlib
·
Related projects
archABM | architectural agent based modeling
#agent-based simulation
simJS | process-based discrete-event simulation framework
#agent-based simulation
privacy preserving contact tracing for COVID19
#agent-based simulation
bus routing agent based simulation
#agent-based simulation #transportation